How Will I Receive My Loan
When your loan is disbursed, your school will take out sufficient funds to pay for tuition, room and board and any other fees. If there is any money remaining from your loan proceeds, your schools financial aid office will refund it to you within 14 days. Remember, funding from student loans can only be used for legitimate educational expenses.
Is There Anything Else I Need To Know
Both subsidized and unsubsidized loans have a loan fee, which is a percentage of the total loan amount that is subtracted from each disbursement you receive. It is your responsibility to pay back the full amount you borrowed, not just the amount you received less the loan fee. For loans disbursed on or after October 1, 2015 and before October 1, 2016 the loan fee is 1.068%.
Pros And Cons Of Direct Unsubsidized Loans
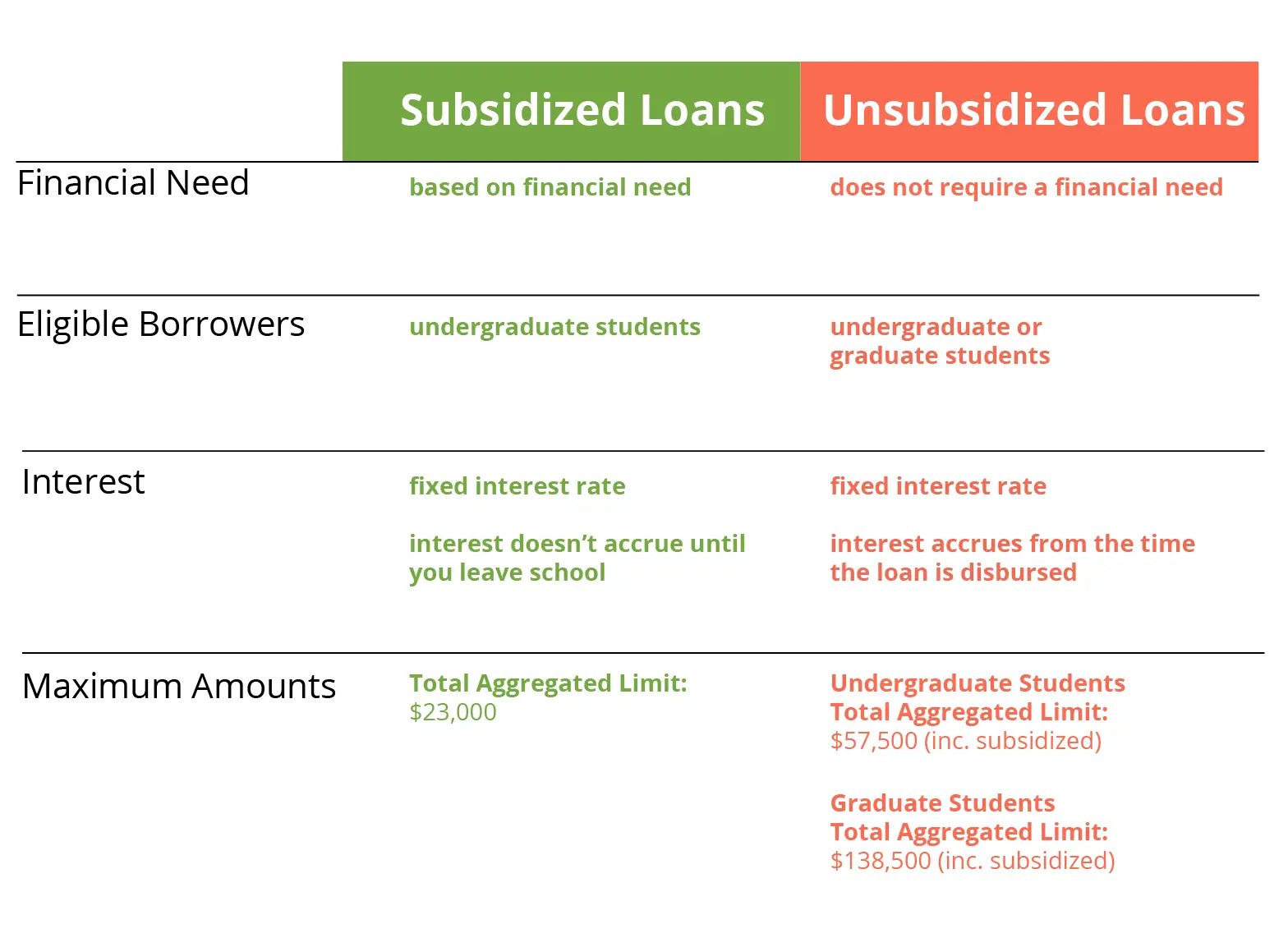
Unlike Direct Subsidized Loans, which are only for lower-income undergraduate students, Direct Unsubsidized Loans are for both undergraduate and graduate students, regardless of financial need.
Unsubsidized loans have relatively low interest rates. The rate is 5.28% for graduate borrowers and the same rate as subsidized loans for undergraduate borrowers . In addition, unsubsidized loans have higher annual and aggregate borrower maximums.
Direct Unsubsidized loans share many of the same benefits as Direct Subsidized Loans, including income-driven repayment plans and the potential for loan forgiveness. However, the borrower is responsible for all interest that accrues on unsubsidized loans, starting immediately as soon as the loan is disbursed. Interest is also capitalized, meaning the amount of accrued interest is added to your principal at certain times, such as the end of your grace period. Interest then accrues on the new higher balance, causing your balance to grow faster. Over time, interest capitalization can increase your total repayment cost.
Recommended Reading: Fha Mortgages Refinance
Pros And Cons Of Direct Unsubsidized Loan
As is the case with all student loans, the Direct Unsubsidized Loan has both positive and negative aspects. To learn what they are, check the following list of this loans pros and cons:
Pros:
-
Higher Loan Limits
Compared to other types of loans, this one allows students higher loan limits, so they wont worry about financing their higher education.
Designed for Graduate and Undergraduate Students
What do unsubsidized loans for both graduate and undergraduate students mean is that no matter your level of higher education, youll still be eligible for financial means to cover your tuition expenses.
Financial Need Proof Not Needed
Most students have low or no credit score at all, so having a loan option that doesnt require them to provide information about their financial situation is very convenient.
Repayment Plan Option
Compared to private loans, federal loans come with repayment plans based on your income, as well as with certain protection in case of default.
Cons:
-
Interest
Do subsidized loans have lower interest rates? Although the interest rate for unsubsidized loans is rather low, it must be paid by the borrower, in contrast to subsidized loans, the interest of which is covered by the Federal Government.
You can choose to pay the interest while attending school or wait until after you finish your education, when it will be capitalized .
Limited Loan Amounts
Repaying Federal Direct Loans

Youll begin repaying your loans six months after you graduate or drop below half-time status. First, youll be asked to complete exit counseling, which will provide you with information on repaying your loans. Well send you email with the details when its time for you to go through exit counseling.
Also Check: Fha Loan Limits In Texas
To Receive Your Subsidized Or Unsubsidized Loan:
Loan Proration For Graduating Undergraduate Students
If you are a graduating senior and only attending one semester, your Federal Direct loans may be prorated based on the number of credits for which you are enrolled. This means that you may not be eligible to receive your maximum annual loan limit.
This affects students enrolled for only one final semester in an academic year: either fall-only, spring-only, or summer-only. For example, this will not affect students who are enrolled in fall and spring semesters and graduate at the end of the spring semester.
You May Like: Mortgage Loan Originator License California
Federal Direct Subsidized And Unsubsidized Loans
A loan is money you borrow and must pay back with interest. Borrowing can be costly. We recommend you consider borrowing only if you have exhausted all other options and only borrow what you need. Make a budget for yourself to keep your debt within manageable limits. An undergraduate financial aid offer may include a combination of Federal Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized loans.
Some loans are need-based others are available to any enrolled student. Although loan terms may vary, Temple uses a scheduled academic year that begins with the fall semester. The academic year is 30 weeks in length and is defined as fall semester , spring semester with summer sessions as a trailer.
Loan Limits On Unsubsidized Student Loans
Unsubsidized loans generally allow higher loan limits than on subsidized loans, letting students borrow more money.
An independent undergraduate student will qualify for a higher loan limit than a dependent undergraduate student on an unsubsidized federal student loan. Dependent undergraduate students may qualify for the same limits as independent students if their parent was denied a Federal Parent PLUS Loan due to an adverse credit history.
Federal student loans have an annual loan limit per academic year, and an aggregate loan limit, which is the total amount a student can borrow for their education.
Also Check: Usaa Apply For Auto Loan
Paying For Higher Education
In order to help cover the costs of higher education, including four-year university, community college, trade schools, technical schools, or career schools, the federal government offers both subsidized and unsubsidized student loans through the U.S. Department of Education. These are direct loans, and are sometimes referred to as Stafford Loans, or Direct Stafford Loans. Lets take a look at subsidized loans first.
Should You Make Interest Payments While In College
Those students utilizing the Federal Unsubsidized Loans often ask whether it is a good idea to begin making payments while the student is in school rather than waiting until the required payments start.
The answer is yes, if they can manage it financially.
The analysis below shows how making voluntary payments early will effect the borrowers bottom line.
This analysis assumes that your student is taking the full loan all four years of college, it assumes that the loans are disbursed at the beginning of each semester, and it also assumes an average interest rate of 4.5 percent.
This chart shows the difference between making monthly interest-only payments, quarterly interest-only payments, an annual interest-only payment, and making a payment larger than the interest amount.
Don’t Miss: Usaa Loan Approval
Cons Of Subsidized Federal Student Loans
- The borrower has to demonstrate financial need, and a parents income and assets might disqualify a student from receiving a subsidized loan.
- Graduate and professional students are not eligible.
- Borrowing limits are lower, and the student might have to supplement with other loans.
- Unpaid loan balances dont go away in bankruptcies.
What Does An Unsubsidized Loan Mean

Most other educational loans are unsubsidized. The Federal Direct Loan program offers unsubsidized student loans PLUS and private loans are also not subsidized.
With an unsubsidized student loan, the borrower is responsible for making interest payments as soon as the loan is issued.
This could mean paying interest payments during school, or it could mean adding those interest payments to the principal of the loan, to be repaid after graduation.
Direct Unsubsidized Loans are not based on financial need, and are available to graduate students as well as undergraduates. They have fixed interest rates, and students need to fill out the FAFSA to apply.
The aggregate cap for Direct Unsubsidized Loans is $31,000 total. Interest is due immediately, even during the post-graduate grace period and during deferment or forbearance, although it can be added to the principal instead of being paid right away.
Other unsubsidized loans have their own terms and conditions.
PLUS loans are also through the federal government, and private loans are available from a variety of lenders.
In all cases, however, you will find the interest either due during school or added to the balance of the loan and due during repayment.
You May Like: 646 Credit Score Car Loan
Interest Rates On Subsidized And Unsubsidized Loans
The federal government sets federal student loan interest rates, and the rates may change each school year. For the 2021-22 academic year, the interest rates are:
- 3.73 percent for undergraduate students who take out Direct Unsubsidized or Direct Subsidized Loans.
- 5.28 percent for graduate and professional-degree students who take out Direct Unsubsidized Loans.
Subsidized And Unsubsidized Loan Examples
Example 1:
Alberta Gator is a first year dependent undergraduate student. Her cost of attendance for Fall and Spring terms is $17,600. Albertas expected family contribution is $10,000 and her other financial aid totals $9,000.
Because Albertas EFC and other financial Aid exceed her Cost of Attendance, she is not eligible for need-based, Subsidized Loans. She is, however, eligible for an Unsubsidized Loan. The amount she would be awarded would be $5,500. Even though her cost of attendance minus other financial aid is $8,600, she can only receive up to her annual loan maximum .
You May Like: Usaa Auto Refi Rates
If You Reach The Subsidy Limit And Lose The Interest Subsidy You Become Responsible For Interest On Your Subsidized Loans In Your Current Program In Certain Situations
- While enrolled in school at least half time
Before
-
Afterlosing the interest subsidy
Note that if you enroll in a longer program after previously losing your subsidy, you may become eligible for additional subsidized loans up to your new, longer, subsidy limit. However, you are still responsible for interest that is accruing on your previous loans that lost the subsidy.
In addition, any loan that lost subsidy and which has been paid in full is not eligible for retroactive subsidy reinstatement.
Choosing The Perfect Loans For You
When you are ready to enroll in college, recognize that applying for direct subsidized loans are likely to be a part of the process. These typically have the lowest interest rate and the easiest reasonable qualifications. They may be more affordable than many private student loans. Start with direct subsidized student loans as these typically allow the government to cover the cost of interest. Then, consider unsubsidized student loans before you choose private student loans.
You may also want to talk to your school about other ways to reduce what you owe. Work study may be one option. Your financial aid office may offer insight on other options available, including Direct Plus Loans. This may be very helpful for most many students, including dependent undergraduate students.
A federal direct subsidized loan is just one way for you to help cover the cost of your college education. The terms and interest rates, as well as the fees and loan amounts, may change over time. However, these loans provide you with an affordable way to secure the funds you need to pay for your educational needs. For that reason, many students should look into them apply for the FAFSA, and then select the best loans for their needs. Work to reduce costs by ensuring repayment options fit your budget. Remember that entrance counseling and the financial aid office may help you with any questions and concerns you have regarding these loans.
Find Student Loans
Also Check: Upstart Vs Avant
Ok So How Do Loans Work
The way that loans work is pretty standard, no matter where you’re getting the loan from. You borrow a sum of money, or principal, from some lenderusually a bank. You also agree to particular loan terms, including interest rates and length of repayment.
When you make loan payments, which usually happens on a monthly basis, you pay back a portion of the principal plus extra money: the interest, or a percentage of the principal that’s accrued . The longer you take to pay back the loan, the more interest accrues. The bigger your principal, the more interest accrues.
You can think about interest as a charge or a fee that you pay to your lender. Interest is how lenders make money on loans. It usually starts accruing as soon as the loan is disbursed (when the money is given out, or provided to you.
Sometimes, the interest that has accrued on your loan is added to your principle. When new interest accrues, it will be on this new, larger principle. This is called capitalizationwhen this happens, you start paying interest on more than your original loan amount, which means more interest.
Loans can be really helpful when it comes to paying for school, but as you may have guessed, people generally don’t love being in student debt. The less money you owe after you graduate, the better, right?
How Direct Subsidized Loan Funds Are Distributed
If you are a first-time Direct Loans borrower, you will be required to attend entrance counseling before your loan funds are sent to your school. Some schools require in-person counseling, but many offer online counseling. You will learn about the loan terms, conditions, and requirements during the counseling session.
You will also be required to sign a Master Promissory Note before the loans can be disbursed.
The Direct Loan program sends the funds to your school to be credited to your student account. In most cases, the loan will be sent in at least two installments.
Special reminder: There is typically a 30-day delay in disbursing student loans to first-time, first-year borrowers.
Loan funds are credited to your account in this order:
If any loan funds remain in your account, the credit balance will be refunded to you by check, cash, debit card, or electronic funds transfer to your bank account. Remember, the refund must be used to pay for your direct and indirect education expenses, such as textbooks, supplies, and equipment.
Read Also: How Long Does A Sba Loan Take
Why You Can Trust Bankrate
Founded in 1976, Bankrate has a long track record of helping people make smart financial choices. Weve maintained this reputation for over four decades by demystifying the financial decision-making process and giving people confidence in which actions to take next.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy, so you can trust that were putting your interests first. All of our content is authored by highly qualified professionals and edited by subject matter experts, who ensure everything we publish is objective, accurate and trustworthy.
Our loans reporters and editors focus on the points consumers care about most the different types of lending options, the best rates, the best lenders, how to pay off debt and more so you can feel confident when investing your money.
Pros Of Unsubsidized Student Loans
- Undergraduate, graduate and professional students are eligible.
- Unsubsidized loans come with higher loan limits than subsidized loans.
- Borrowers and families dont need to demonstrate financial need to qualify.
- Its possible to defer payments for up to six months after graduating or leaving school .
- The loans include federal student loan benefits, like multiple repayment options.
- No credit check is required.
Don’t Miss: Typical Motorcycle Loan
What About Interest Rates
Whether you choose subsidized or unsubsidized loans, or both, youll want to know what interest rate youll be paying. According to the U.S. Department of Education, the interest rate for loans disbursed after 7/1/17 and before 7/1/2018 are as follows:
| Unsubsidized vs. Subsidized Interest Rates |
| Loan Type |
| 6% |
What Happens When My Subsidy Is Lost
If you reach the subsidy limit, you’ll get a letter from your servicer notifying you that you have lost your subsidy. But what does it mean to lose the subsidy benefit?
- You aren’t eligible to take out any more subsidized loans for your current program. However, this does not affect your eligibility for unsubsidized loans.
- The interest on your existing subsidized loans is no longer subsidized by the government when you’re in school, a deferment, or in certain income-driven repayment plans. This means you are responsible for all interest that accrues on your subsidized loans moving forward, as of the date of your continued or new enrollment.
- You aren’t required to make payments on the interest that accrues while you are in school. If you don’t pay the interest that’s accruing on your loans, it will capitalize, or be added to your principal balance at the end of your grace period or deferment. Capitalization costs you more in interest over the life of your loan. Making payments while you’re in school can save you money in the long run.
You May Like: Strongly Recommended For First Time Buyers
Subsidized Loan Vs Unsubsidized Loan
Unlike subsidized loans wherein the lender pays the interest that accrues on the loan during certain periods, unsubsidized loans hold the borrower responsible for paying interest on the loan during all periods.
Direct Unsubsidized Loans offered by the U.S. Department of Education are a common example. You’ll have to pay any interest that accrues while you’re in school and during grace periods or deferments, resulting in higher total loan costs and monthly payments than you would rack up with a subsidized loan, as the earlier example of the two students shows. The cost differential increases if the recipient of an unsubsidized loan opts not to pay interest during school, which triggers capitalization. A student who takes out a subsidized loan won’t pay interest that accrues during these periods or face capitalization.
Going back to the earlier example, let’s say that Jenny took out a Direct Unsubsidized Loan with the same terms as Joe’s Direct Subsidized loan. As such, she’s on the hook to pay any interest that accrues on her loan for four years. Moreover, she opts not to pay interest while in school, so any unpaid interest is capitalized or added to the loan principal. Jenny already has $10,821 debt at the start of repayment after accounting for interest accrual and capitalization. Over a 10-year repayment period, Jenny pays a higher monthly payment of $103.
