Loan To Value Ratio Meaning
The Loan to Value ratio is a risk assessment tool for lenders, signifying the extent of risk they would be at if they approve a loan amount to seekers with respect to the propertys value, which acts as collateral. The lenders or creditors consider this ratio before approving any mortgage loan application. If the ratio is good to go, the loan seekers receive approval.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc., Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be HyperlinkedFor eg:
A higher LTV would mean a higher risk involved with the mortgage loan deal. In such a scenario, the lenders ask loan seekers to buy mortgage insurance against the approval to mitigate this risk associated with the same.
Ways To Potentially Increase Your Equity
If your homeâs value remains stable, you can build equity by paying down your loanâs principal. If your payments are amortized , this happens automatically, simply by making your monthly payments. To lower your LTV ratio more quickly, consider paying more than your required payment each month. This helps you chip away at your loan balance.
Also, protect the value of your home by keeping it neat and well-maintained. Smart home improvements can help, too. However, itâs a good idea to consult an appraiser or real estate professional before investing in any renovations you hope will increase your homeâs value. Remember that economic conditions â and the normal dips and swings of the real estate market â can affect your homeâs value no matter what you do. If the value of your home increases due to a renovation project, your LTV ratio could drop, depending on how much equity you tapped to cover the costs. But falling home prices in your area could cancel out the value of any improvements you might make.
Building up the equity in your home can help you pursue other important goals and provide a financial buffer in case of emergencies. The first step to taking advantage of it is knowing how much you have.
This article was adapted from Better Money Habits®. Visit BetterMoneyHabits.com for more practical financial information.
Make A Larger Down Payment
When buying a home, making a larger down payment will lead to a lower LTV. Lenders and mortgage investors take your down payment as one indicator of the risk involved in your loan. From a lenders perspective, when home buyers invest more of their own funds upfront, lenders will see them as serious and invested borrowers.
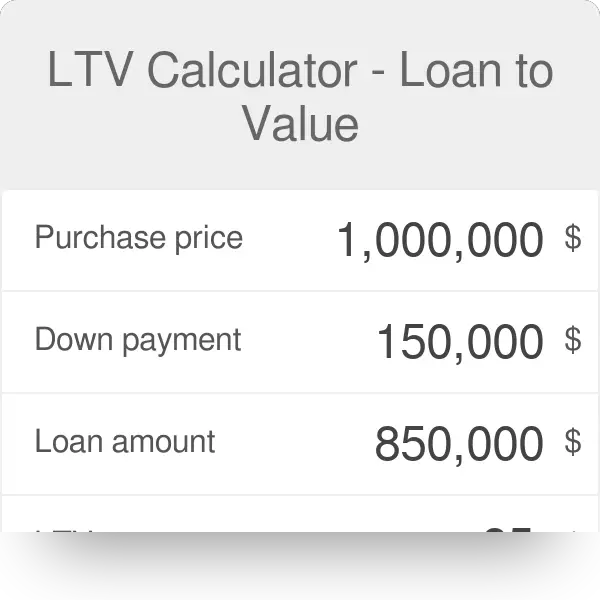
Larger down payments also increase equity in the home. For example, if youve put $20,000 down on a home appraised for $100,000, your LTV on an $80,000 loan will be 80%. The larger the down payment, the smaller your LTV ratio .
Heres an example of how a larger down payment can decrease your loan-to-value ratio.
Also Check: What Is The Jumbo Loan Limit For 2021
Why Is Ltv Important
Having a lower LTV ratio will not only help you qualify for a loan, but it will allow you to access lower mortgage rates, which can save you thousands of dollars over the life of your loan. And, a desirable LTV ratio can ensure you dont have to pay monthly mortgage insurance, which can increase your mortgage by hundreds of dollars each month.
What Is A Combined Loan To Value Ratio

When borrowers secure financing through multiple loan programs, lenders often consider the combined loan to value ratio in addition to the loan to value ratio.
CLTV measures all of the outstanding balances on a commercial propertys loans against the propertys value. Whereas LTV considers only one loan against the property, CLTV considers all loans that are secured with the property.
Combined Loan to Value Ratio = All Loan Balances / Property Value
The combined ratio provides a more comprehensive measure when multiple loans and/or lines of credit are being used. Its unnecessary when using only one loan.
Don’t Miss: Can You Change Loan Type Before Closing
What Is A Loan
The loan-to-value ratio of a loan is how much money youre borrowing compared to the value of the asset securing the loan. In the case of a mortgage, it compares the remaining balance of your loan to the value of your house. On an auto loan, it compares the balance of your loan to the value of your car.
Lenders use LTV as a way to measure the risk of a loan. The lower a loans LTV, the less risk the lender is taking. If you fail to make payments and the lender forecloses, a lower LTV ratio means the lender has a higher chance of fully recovering their losses by selling the foreclosed asset. A higher LTV means more risk the lender loses some money.
Lenders may have maximum LTVs that theyll approve. For example, FHA loans require at least 96.5% LTV. Conventional loans require at least 97% LTV, but only for the best-qualified borrowers most require 95% LTV or lower. Your loans LTV can have other important impacts on your borrowing experience, including your interest rate and monthly payment.
What Is A Loan To Value Ratio
Imagine that you want to buy a house. You can’t afford it, though, unless you take a mortgage – the property costs $200,000. You have analyzed your finances and decided that you have $20,000 available for the down payment.
LTV describes the ratio between the loan amount and the total purchase price. It means that, in this case, you will have to follow the steps below.
Subtract the down payment from the total price to obtain the loan amount:
$200,000 – $20,000 = $180,000
Divide the loan by the total price:
$180,000 / $200,000 = 0.90
Finally, multiply this value by 100% to obtain LTV:
LTV = 0.90 * 100% = 90%
You May Like: How To Ask For Student Loan Forgiveness
Loan To Value Vs Debt Service Coverage
Debt service coverage ratio focuses on interest rates and amortization schedules. This metric is almost entirely insulated from changes in property value.
Loan to value doesnt assess the financials of a loan itself in the same way that DSCR does, but instead examines the loans amount as it relates to the property.
How Is Cltv Calculated
Your CLTV is calculated by adding up all loan balances related to a property and dividing the sum by the appraised value. Heres an example. Lets say you have a remaining balance of $200,000 on a home thats worth $350,000. Your LTV in that case would be $200,000 divided by $350,000: a 57% loan-to-value ratio. But you also have a HELOC on the property with a balance of $30,000 and a home equity loan you still owe $40,000 on. That means you owe $270,000 in total . Divide that total amount of $270,000 by the property value of $350,000, and your combined loan-to-value ratio is 77%.
Appraised home value: $350,000
Total amount Owed: $270,000
LTV formula: $270,000/$350,000 = 0.77 or 77% LTV
An LTV of 57% is great, and while a CLTV of 77% is still good, it may have different risk implications for your lender.
Also Check: What Size Loan Do I Qualify For
How Lenders Use Ltv Ratios
A loanâs LTV ratio is one factor lenders might use to help make decisions about loan applications, rates and terms. A higher LTV ratio is riskier for lenders. More of their money is on the line, and the borrower may be less invested in keeping up with their payments.
Consider someone who buys a $400,000 home with 5% down, an LTV of 95%. If the housing market drops, this person might have a $380,000 mortgage for a home thatâs now worth $350,000âtheyâre âunderwaterâ on the loan. They may decide that their best course of action is to stop making payments and let the home go into foreclosure, even if it will hurt their credit.
If the lender had required a larger down payment, which resulted in a lower LTV, the borrower might have more money at stake and be less inclined to walk away from the home.
What About A Combined Loan
A combined loan-to-value ratio is the ratio of all loans on a property to the value of that property. Unlike an LTV, which looks at the ratio of a single loan to a propertys value, a combined LTV includes the LTV mortgage plus any lines of credit, home equity loans, second mortgages, or liens. Unlike LTV ratios, many institutions are willing to lend at a CLTV ratio of 80% or higher if the applicant have good credit ratings.
Our financial calculators are provided as a free service to our Members. The information these calculators supply is from various sources based on calculations we believe to be reliable regarding their accuracy or applicability to your specific circumstances. All examples are hypothetical and illustrative and do not intend to provide investment advice. TDECU does not accept any liability for loss or damage whatsoever, which may be attributable to the reliance on and use of the calculators. Use of any calculator constitutes acceptance of the terms of this agreement. TDECU recommends finding a qualified professional for advice about your personal finance issues.
Don’t Miss: Does Credit Score Matter For Va Loan
How Do You Calculate Loan To Value
Typically a loan-to-value ratio should be 80% or less to avoid adding PMI.
- Loan Amount ÷ Current Appraised Value = LTV
What Is A Good Ltv Ratio For A Mortgage
Generally, a good LTV to aim for is around 80% or lower. Managing to maintain these numbers can not only help improve the odds that youll be extended a preferred loan option that comes with better rates attached. It can also boost your chances of being able to avoid paying mortgage insurance and potentially being able to save thousands of dollars in mortgage payments.
Although this is ideal, its not always possible, particularly for first-time home buyers. Its possible to qualify for a conventional loan with as little as 3% down.
Should your LTV come in higher than 80%, youll likely have to pay extra for private mortgage insurance on a conventional loan. Mortgage insurance basically serves as a form of risk mitigation for lenders that helps protect them in case you default on the loan and helps provide them with needed reassurance if they opt to take on the risk of lending to you.
Read Also: 401k Loan Interest Rate 2021
More Ltv Ratio Rules To Know
Your lender may limit you to a lower LTV ratio if youre buying or refinancing a rental property, a manufactured home, a two- to four-unit home or a second home. On the other hand, you may be able to borrow more than the limits listed above if:
- Youre taking out a home equity loan or home equity line of credit
- Your home is worth less than your mortgage balance and youre eligible for a Home Affordable Refinance Program replacement loan.
- Youre applying for Fannie Maes Community Seconds mortgage program or a down payment assistance program that lets you borrow up to 5% more than your home is worth.
How To Calculate Loan To Value Ratio
Lenders often compare the total dollar value of their loan to what the borrower is contributing, which is the value of the property securing the loan.
The loan to value ratio measures the relationship between two factors:
The loan to value ratio is a metric frequently calculated by financial institutions and lenders to measure credit risk, particularly when considering mortgage applications.
The loan to value ratio can be calculated by dividing the loan amount by the appraised property value.
Don’t Miss: Why Mortgage Companies Sell Your Loan
Combined Loan To Value Calculation
The combined loan to value measures two mortgages combined against the appraised property value.
For instance, lets assume that you already have a mortgage but have decided to apply for another.
The lender will evaluate the combined LTV , which factors in the following:
If the current outstanding loan balance is $240,000 on a recently appraised home at $500,000, but now you want to borrow an additional $20,000 in a home equity loan for backyard renovations, the CLTV formula is as follows.
- Combined Loan To Value = / $500,000
How Do You Calculate Loan
Divide the amount of the loan by the appraised value of the asset securing the loan to arrive at the LTV ratio.
As an example, assume you want to buy a home with a fair market value of $100,000. You have $20,000 available for a down payment, so you’ll need to borrow $80,000.
Your LTV ratio would be 80%, because the dollar amount of the loan is 80% of the value of the house, and $80,000 divided by $100,000 equals 0.80 or 80%.
Read Also: How To Get Home Loan Pre Approval
What Are Disadvantages Of Loan
The main drawback of the information that a LTV provides is that it only includes the primary mortgage that a homeowner owes, and does not include in its calculations other obligations of the borrower, such as a second mortgage or home equity loan.Therefore, the CLTV is a more inclusive measure of a borrower’s ability to repay a home loan.
What Is The Formula For Calculating The Loan
Secured loan amount
To calculate the loan-to-value ratio, divide the amount of the loan being requested by the market value of the asset that the business gives as collateral to the lender.
The market value may be lowered if the asset has low liquidity, that is, if it could take time before the financial institution can have the money on hand. This length of time often comes with associated costs, such as hiring a real estate broker to look at a building. The institution factors that in by reducing the market value.
The market value given to an asset varies depending on the context and the financial institution.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Out Of Underwater Car Loan
Home Mortgage Loan Assumptions
Suppose you have decided to purchase a home currently worth $400,000 in the market based on a recent appraisal.
Since you do not have enough cash on hand to purchase the house all by yourself, you resort to getting assistance from a bank that offers to provide 80% of the total purchase price, i.e. $320,000.
The remaining 20% must be paid out of your pocket.
- Mortgage Loan = $320,000
- Down Payment = $80,000
What Is A Good Loan To Value Ratio
When qualifying for a mortgage loan, an 80% loan-to-value ratio is ideal because it minimizes a lenders risk of losing money if the borrower defaults. Thats why home buyers with 20% down, and an 80% LTV, get special perks like avoiding mortgage insurance.
From a lenders perspective, a lower LTV is always better, says Meyer.
But and its a big but it doesnt always make sense to aim for 80% LTV. Because a 20% down payment is simply not doable for many home buyers, especially first-time home buyers.
Therefore, a good loan-to-value ratio depends on your home buying goals. For one person, 100% might be a good LTV. For another, 70% might be ideal.
Heres what to consider.
If your goal is to make a small down payment and buy a home sooner, look for one of these mortgage programs with high LTV ratio allowances:
- FHA loan: 96.5% LTV
If your goal is to avoid higher interest rates, get the lowest monthly payment on your loan, or minimize your overall loan closing costs, you should aim for a lower LTV. This usually means getting a conventional mortgage with 10%-20% down.
You May Like: How Much Down Payment For Home Loan
Definition And Example Of Loan
A loan-to-value ratio tells you how much of a property you truly own compared to how much you owe on the loan you took out to purchase it. Lenders use LTVs to determine how risky a loan is and whether they’ll approve or deny it. It can also determine whether mortgage insurance will be required.
- Acronym: LTV ratio
For example, if you buy a home that appraises for $200,000 and make a down payment of $20,000, you are borrowing $180,000 from the bank. The loan-to-value ratio on your mortgage would then be 90%.
The ratio is used for several types of loans, including home and auto loans, and for both purchases and refinances.
LTVs are part of a bigger picture that includes:
- Your credit score
- Your income available to make monthly payments
- The condition and quality of the asset youre buying
It’s easier to get higher LTV loans with good credit. In addition to your credit, one of the most important things lenders look at is your debt-to-income ratio, your debt payments divided by your income. This is a quick way for them to figure out how affordable any new loan will be for you. Can you comfortably take on those extra monthly payments, or are you getting in over your head?
How Ltv Affects Your Mortgage Rates
Lenders use LTV as a way to measure the risk of a loan. The higher the LTV of a loan, the higher its risk.
Lenders compensate for risk in a few ways.
One is that they tend to charge higher interest rates for riskier loans. If you apply for a loan with a high LTV, expect to be quoted a higher interest rate than if you were willing to make a larger down payment. A higher rate raises your monthly payment and the overall cost of your loan.
Another is that lenders may charge additional fees to borrowers who apply for riskier loans. For example, you might have to pay more points to secure an affordable rate, or the lender might charge a higher origination fee. A larger down payment might mean lower upfront fees.
One of the most significant impacts of a mortgages LTV ratio is private mortgage insurance . While PMI does not affect the interest rate of your loan, it is an additional cost that you have to pay. Many lenders will make borrowers pay for PMI until their loans LTV reaches 80%.
PMI can cost as much as 2% of the loans value each year. That can be a big cost to add to your loan, especially if you have a large mortgage.
You May Like: Online Loans That Are Legit
