Federal Direct Student Loans
The table below shows the breakdown of the maximum amount you can borrow when taking out direct subsidized and unsubsidized student loans. Note that the total for each year, and cumulatively, includes both subsidized and unsubsidized federal loans. If, for example, your subsidized loan total in year one as a dependent undergrad is $3,500, you are limited to $2,000 in unsubsidized loans for that year. If your subsidized total is less than $3,500, the difference between that and $5,500 can be unsubsidized loans.
The amount you can borrow each year and cumulatively as an undergrad is also affected by your parents’ eligibility to help you by taking out a direct PLUS loan. If they are eligible, the amount you can borrow in your own name is less. If they are ineligible, due to poor credit, for example, you can borrow more. Amounts for independent undergrads also reflect lack of parent supportas do amounts for graduate and professional students, who are always considered to be independent.
| Dependent Undergrads | Subsidized |
|---|---|
| $138,500 |
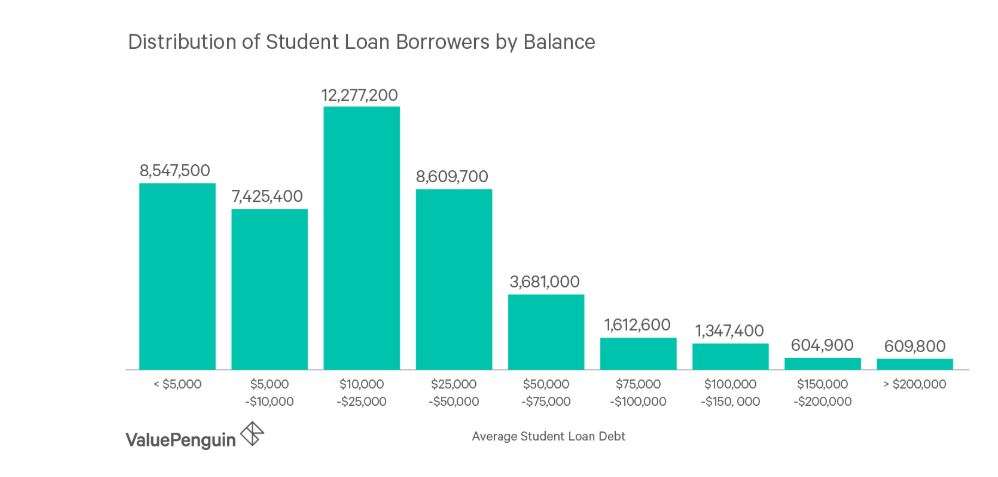
The aggregate total for each class of borrower includes all unpaid loan balances for all federal student loans taken. This includes subsidized and unsubsidized FFEL loans, which are no longer available, in addition to subsidized graduate level loans dispersed before July 1, 2012.
To apply for federal student loans, you’ll need to submit the Free Application for Federal Student Aid .
What Other Help Is Available
Jaylon Herbin, a student loan expert with the Center for Responsible Lending, pointed to two other sources of help the administration offers: expanded loan forgiveness for borrowers who take public-service jobs, and the Fresh Start program for borrowers in default.
Borrowers have until Oct. 31 to apply for the Public Service Loan Forgiveness plan, which wipes out loan debt for people who make timely payments for 120 months while working full time for the government or a qualifying nonprofit organization. The administration extended eligibility retroactively to borrowers with certain types of federal loans that were not previously included, as well as those with federal direct loans who worked for qualified employers but had not certified their eligibility.
You can apply for retroactive inclusion at the Federal Student Aid website youll need the most recent tax form you received from your employer or your companys federal employer identification number. Borrowers with some uncommon types of federal loans will have to consolidate them into a federal direct loan to qualify.
Getting out of default will restore your eligibility for federally backed mortgages and other loans, as well as income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs.
Who Qualifies For Loan Debt Forgiveness
The White House’s plan will forgive federal student loan debt for borrowers who earned less than $125,000 — or less than $250,000 for heads of households or married couples filing jointly. Along with undergraduate federal loans, the plan covers graduate and parent PLUS loans, according the the Washington Post.
Only those student loans provided by the government — including Pell grants — qualify for the forgiveness plan. Private loans made by banks, credit unions or other financial institutions are not included.
Also Check: What Is An Agency Jumbo Loan
How Student Loan Forgiveness Will Be Applied
The Education Department has indicated that it will utilize a waterfall method when applying the $10,000 or $20,000 student loan forgiveness award for borrowers who have larger balances. The department says it will prioritize the application of loan forgiveness in the following order:
- Defaulted Department of Education-held loans
- Defaulted commercial FFEL Program loans
- Non-defaulted Direct Loan Program loans and FFEL Program loans held by the department
- Perkins Loans held by the department.
For borrowers who have multiple loans in a specific type of loan program , the department will apply the relief in this order:
- Loans with highest statutory interest rate will get first priority.
- If interest rates are the same, student loan forgiveness will be applied to unsubsidized loans prior to subsidized loans.
- If the interest rate and subsidy status are identical, the department will apply the loan forgiveness to the most recent loan.
- If the interest rate, subsidy status, and disbursement date are all the same, the department will apply the loan forgiveness to the loan with the lowest combined principal and interest balance.
How Student Debt Affects Your Credit Score
Student loans and lines of credit form part of your credit history. If you miss or are late with your payments, it can affect your credit score.
Your credit score shows future lenders how risky it can be for them to lend you money. A poor credit score can also affect your ability to get a job, rent an apartment or get credit.
Recommended Reading: Best Rates For New Car Loans
Loans That Are Eligible For Student Loan Forgiveness
The Education Department confirmed that nearly all government-held federal student loans, including undergraduate loans, graduate loans, and Parent PLUS loans, can qualify. Government-held loans include all federal Direct student loans, as well as some FFEL-program loans and Perkins loans held by the government. Defaulted federal student loans also qualify.
FFEL-program loans held by private, commercial lenders do not automatically qualify for student loan forgiveness under the Biden initiative. However, the Education Department confirmed that FFEL borrowers can receive this relief by consolidating these loans into the Direct Loan program.
Since Direct loan consolidation does not necessarily make sense for all borrowers, the department is also working on a fix to potentially expand access to FFEL borrowers without needing to consolidate.
What Happens If You Hit Federal Loan Limits
If your cost of attendance exceeds what you can borrow in federal student loans, you may not have enough cash on hand to cover the extra costs. If youre worried about not having enough money to pay for school, you have a few options, including:
Working part-time. Find a job that lets you work non-traditional hours so you can pay for school. You can look on- or off-campus, depending on your living situation and transportation options. Consider a side-hustlelike delivering groceries, tutoring or freelancingto cover your extra schooling costs.
Requesting payment assistance. Many schools require payment in full, whether that comes from your lender or you. If you cant pay your outstanding bill, talk to your schools financial aid office about a payment plan, like making monthly payments instead of one lump-sum payment. Also inquire about emergency grants or interest-free loans, which vary by school but might be available based on your need.
Switching schools. Cost of attendance varies by each school. Since every institution has different service fees, you might pay more at a private or big-name school compared to community colleges, which tend to have fewer fees. If you can, consider attending local colleges for the first couple years and then transferring to your school of choice to complete your bachelors degree.
Read Also: Is It Worth It To Refinance Car Loan
The Types Of Loans You Have
Federal Direct loans issued by the U.S. Department of Education offer a wide variety of payment options, including a standard repayment plan as well as income-driven plans that cap payments as a percentage of income. If you want the most flexibility in the amount of your monthly student loan payment, focus on exhausting eligibility for federal loans before taking on other kinds of educational debt.
Parent PLUS loans are federal loans offered to parents or guardians of students. While they have some benefits that federal loans have, they generally have a higher interest rate than undergrad and graduate student loans.
Private student loans don’t offer as much flexibility as federal loans once you’ve borrowed since you’re committing to your repayment plan for the duration of the time you have your loan. But when you are choosing a lender, you have a wide variety of different student loan repayment timelines you can choose from, such as loans with five-year, seven-year, or 10-year terms.
Associates Student Loan Payments
Student borrowers with Associates degrees are the most likely to pay off their student loans faster than other degree holders. From a purely financial stand-point, this gives the average Associates degree the highest value in terms of cost-benefit ratio.
- Just 41% of Associates degree holders who graduated from public institutions use student loans to pay for school.
- 84% of attendees of private, nonprofit schools take on student loan debt.
- 88% of attendees of private, for-profit schools take on student loan debt.
- $46,100 is the average annual salary for a recently graduated Associates degree holder.
- $33,800 is the low-end average annual salary.
- 4 to 7+ years is the projected student loan debt repayment period for Associates degree holders who graduate in 2021.
| Monthly Payment |
|---|
| $33,200 |
You May Like: What Form Is Student Loan Interest Reported On
Student Loan Forbearance Or Deferment
If you need more time to repay your loans after the federal pause ends, youll have to ask your lender to put your loans into either forbearance or deferment. Loan forbearance allows you to postpone monthly payments for specific periods but, depending on the forbearance program, interest on your loan may still accrue.
In contrast, loan deferment is a federal repayment program that allows you to pause or reduce your student loan payments for up to three years. Depending on the type of loan you have, you may or may not be responsible for interest charges that accrue on your loan. For both forbearance and deferment, you will need to apply with your loan servicer and meet eligibility requirements.
How Will My Monthly Payments Be Affected
Once payments resume in January, borrowers enrolled in income-driven repayment plans whose debts are not completely forgiven will pay the same percentage of their income that they paid before the pandemic-related moratorium. In other words, unless their income is lower, the debt relief wont lower their payments.
But by reducing the total that borrowers owe, the relief plan could cut the number of years it will take to pay off their debts.
For borrowers enrolled in standard plans who owe more than will be forgiven, the new relief offers a choice:
- Continue making the same monthly payments but pay off their loans sooner, or
- Reduce monthly payments but stick with the 10-year payoff period. If you fall into this category, you should contact your loan servicer to discuss your options while waiting for the forgiveness to take effect.
You May Like: How Much House Loan Do I Qualify For
Q Are Student Loan Burdens Economically Handicapping An Entire Generation
A. More adults between 18 and 35 are living at home, and fewer of them own homes than was the case for their counterparts a decade or two ago. But these trends are mostly due to these folks entering the work force during the Great Recession rather than due to their student loans. Federal Reserve researchers estimate that 20% of the decline in homeownership can be attributed to their increased student loan debt the bulk of the decline reflects other factors.
Dont Miss: How To Get Instant Loan Online
Student Loan Forgiveness: Eligibility Could Be Blocked If You Did This
President Joe Biden announced the much anticipated and widely lauded administrations plan for loan forgiveness on Aug. 24. However, beyond the framework announced at the time, details are still scant, potentially creating a slew of issues and some confusion for borrowers.
Find: How Bidens Student Loan Forgiveness Plan Can Boost Retirement Savings
Under the plan, there will be up to $10,000 in federal student debt relief for most borrowers, up to $20,000 for recipients of Pell Grants, as well as an extension of the payment pause one final time to Dec. 31., according to a White House fact sheet.
But now, several student loan companies are offering borrowers the option to refinance to private loans, which could prevent them from getting debt relief, Insider reported, adding that this prompted the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau to say it raises serious concerns.
According to Insider, several loan companies sent emails to borrowers after Bidens announcement breaking down the difference between federal and private student loans, and offering its refinancing tool to borrowers that would offer lower interest rates. While the switch to a private loan might provide lower interest rates, the refinancing could lead borrowers to miss out on debt cancellation.
As CBS reported, private student loan forgiveness isnt impossible, but its unlikely. After all, Mr. Bidens action is tied to the federal government. Loans owed to private lenders are different.
Recommended Reading: How Much Will I Get Approved For Va Loan
Options For Student Debt Repayment
The Biden-Harris administration also intends to simplify income-driven repayment plans. Currently, income-driven plans adjust your student loan payment to 10% to 20% of your discretionary income while extending your loan terms to 20 or 25 years.
With the latest changes, you could see your payment go down to 5% of your discretionary income for undergraduate loans. Plus, the government could cover your unpaid monthly interest, and your repayment term will only span 10 years. After 10 years, you could see your remaining balance canceled.
While these changes are not yet in effect, you can still apply for various federal repayment plans. These include:
- Standard plan, with fixed payments over 10 years.
- Graduated plan, which spans 10 years and involves payments that start smaller and increase over time.
- Extended plan, with fixed or graduated payments over 25 years.
- Income-driven repayment plans, which include Income-Based Repayment, Pay As You Earn, Revised Pay As You Earn, and Income-Contingent Repayment.
You can also combine your federal loans into a Direct consolidation loan. After consolidating, you can choose any repayment plan or a term of up to 30 years, depending on your loan amount.
Read on for other options for student loan relief worth exploring when the moratorium ends.
How To Pay Off Student Loans
Student loan repayment may look different for everyone depending on your goals and budget. As we approach the end of the moratorium, its a good idea to sign into your student loan accounts and review your balances.
Explore your various options for repayment plans to determine which one works best with your budget. Change your loans to an income-driven repayment plan if youre pursuing PSLF, as those are the only plans eligible for this program.
If you can afford it, consider making extra payments to get out of debt faster and save on interest. One strategy that might help is the debt avalanche method, where you first target loans with the highest interest rate. Another is the debt snowball method, where you prioritize loans with the smallest balances.
Once youre ready to tackle your student loan debt, check out our tips to pay off student loan debt fast.
Also Check: Is Student Loan Relief Real
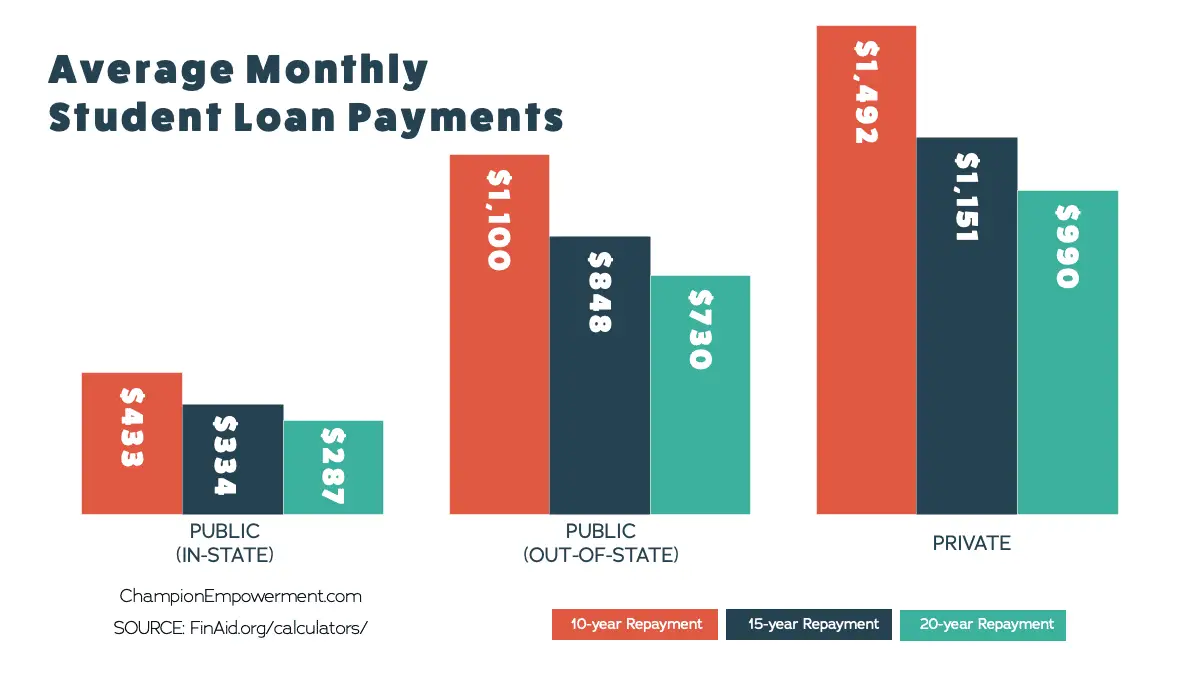
What Is The Average Student Loan Payment Estimate How Much Your Payment Will Be
Want to know how your student loan payment compares to everyone else? This article breaks down the average payment and what yours might be.
Christy Rakoczy Bieber
If you’re thinking about borrowing for school, or if you have already taken out student loans, you may be interested in learning how much the average student loan payment is. Understanding what the typical student pays — and knowing how to estimate your own monthly payments — is important to make sure your loans are affordable.
Here’s the average college loan payment amount, as well as some tips on figuring out how much your loans could cost you.
Pros And Cons Of Debt Cancellation
Moody’s Investor Service predicts wiping out student debt would yield a stimulus to economic activity that is comparable to tax cuts in the near term. Over the longer term, it could increase homeownership and boost the creation of small businesses. Outright debt cancellation would boost real gross domestic product by $86 billion to $108 billion per year, according to one study from Bard College’s Levy Economics Institute.
However, analysts warn of the risk of moral hazard caused by implying that the cost of your decisions will be borne by someone else. This could lead to even higher student debt burdens, as borrowers assume forgiveness will be ongoing.
Another argument suggests that forgiving student loan balances will provide, at best, a weak stimulus to the economy, because the savings are realized in small amounts over a long period, depending on how much a borrower pays back monthly with full or partial forgiveness.
Here are some answers to commonly asked questions about student loan debt in the U.S. and the U.K.
You May Like: How Much Interest Do Loan Sharks Charge
Average Student Loan Debt By State: How Have The Numbers Changed Over Five Years
For the past decade, weve been hearing about the United States massive student loan bubble, with some experts saying the $1.5 trillion in total student loan debt that Americans owe spells doom for the economy, while others declare the fear to be overblown.
With so much emphasis placed on the jaw-dropping nationwide numbers, statistics on how much recent graduates owe state-by-state are often overlooked. This is too bad, though, because the variance in graduate debt by state, and how those numbers have shifted through the years, is one of the more interesting facets of the student loan issue in America.
We looked at the Institute for College Access and Success annual student debt reports the definitive compilation of student loan data from 2017 and 2012 for a closer examination on how the average debt amassed by graduates in each state has fluctuated over the years.
Examining the data, we find an intriguing contradiction: while the average amount of college graduate debt has increased by a double-digit percentage in over half of the 50 states, over 80% of states witnessed no increase or a reduction in the proportion of recent graduates with debt.
How do we make sense of this? Well, tuition costs continue to rise, which explains why students would be compelled to take out larger loans, but the latter figure is something of a mystery. Fewer students are borrowing, yet the ones that do borrow are borrowing more.
Lets take a look at the map:
